Cable joints are critical components in electrical systems, enabling the seamless connection of cables for uninterrupted power distribution. When it comes to cable joint installations, two prominent methods stand out: Cold Shrink Cable Joints and Heat Shrink Cable Joints. Each method offers unique advantages and considerations, making the decision of which to choose a pivotal one.
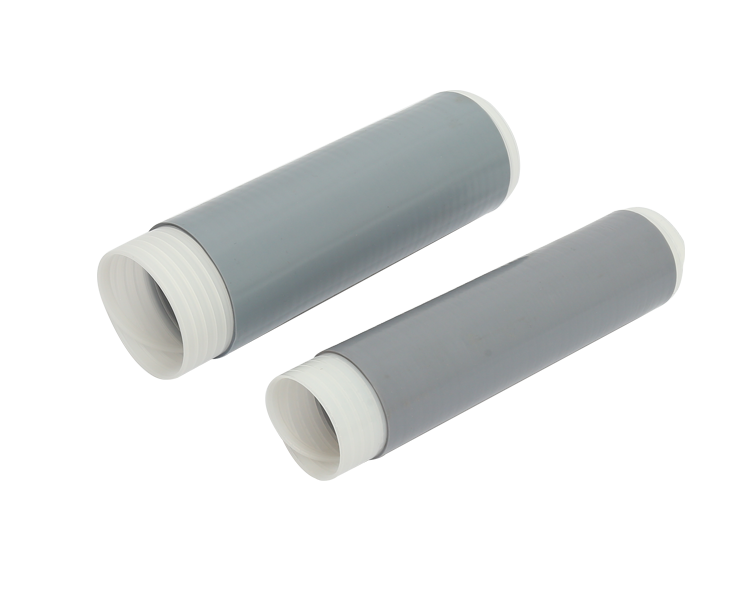
Cold Shrink Cable Joints offer a simplified approach to cable joint installations. These joints are pre-molded, and their installation process involves expanding the tube-like joint over the cable ends and then allowing it to contract into place. Here are the key considerations that make Cold Shrink Cable Joints a suitable choice:
1. Installation Simplicity: Cold Shrink Cable Joints require minimal tools and equipment for installation, making them an ideal choice for situations where complex equipment is unavailable or impractical.
2. Indoor and Outdoor Use: These joints are versatile, suitable for both indoor and outdoor applications. Their weather resistance and UV stability contribute to their durability in diverse environments.
3. Ease of Training: The straightforward installation process of Cold Shrink Cable Joints reduces the need for specialized training, allowing for easier adoption by technicians.
4. Limited Heat Sources: In scenarios where heat sources are unavailable or unsafe, Cold Shrink Cable Joints offer an effective alternative for achieving secure cable connections.
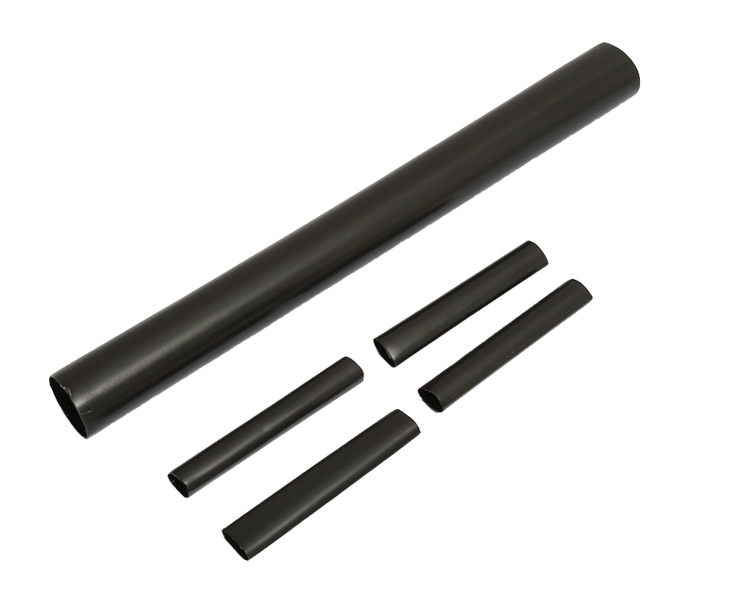
Heat Shrink Cable Joints involve the use of heat to shrink the joint material into place, creating a secure and insulated connection. These joints offer a range of benefits that make them a preferred choice in specific circumstances:
1. Customized Fit: Heat Shrink Cable Joints can be tailored to the exact cable dimensions, ensuring a snug and secure fit that minimizes stress on the cable connection.
2. Complex Cable Configurations: For installations involving complex cable configurations or multiple cores, Heat Shrink Joints provide the flexibility to accommodate intricate cable layouts.
3. High Voltage Applications: Heat Shrink Cable Joints are commonly used in high voltage applications due to their ability to provide enhanced insulation and protection against electrical discharge.
4. Controlled Environments: In controlled environments where heat sources are readily available and safety precautions can be maintained, Heat Shrink Cable Joints offer a precise and reliable option.
Factors Influencing the Choice
When deciding between Cold Shrink and Heat Shrink Cable Joints, several factors come into play:
1. Installation Expertise: The complexity of the installation process can influence the choice. Heat Shrink Joints may require more specialized knowledge and training.
2. Environmental Conditions: Consider the environment where the cable joint will be installed. Cold Shrink Joints are more suitable for extreme outdoor conditions, while Heat Shrink Joints can be tailored for indoor installations.
3. Cable Type: The type of cable being jointed is crucial. Heat Shrink Joints are versatile for different cable types, while Cold Shrink Joints are preferable for a simpler jointing process.
4. Tools and Equipment: Assess the availability of necessary tools and equipment, as Heat Shrink Joints require heat sources for installation.
5. Voltage Level: For high voltage applications, Heat Shrink Joints offer enhanced insulation and protection.
The choice between Cold Shrink and Heat Shrink Cable Joints is contingent upon a variety of factors, including the installation environment, cable type, expertise of technicians, and the availability of tools. Cold Shrink Joints offer ease of installation and versatility, making them suitable for both indoor and outdoor use. On the other hand, Heat Shrink Joints provide customization and enhanced insulation, making them ideal for complex cable configurations and high voltage applications. By thoroughly assessing these factors, installers can make informed decisions that lead to secure, reliable, and long-lasting cable joint installations.

 English
English 简体中文
简体中文