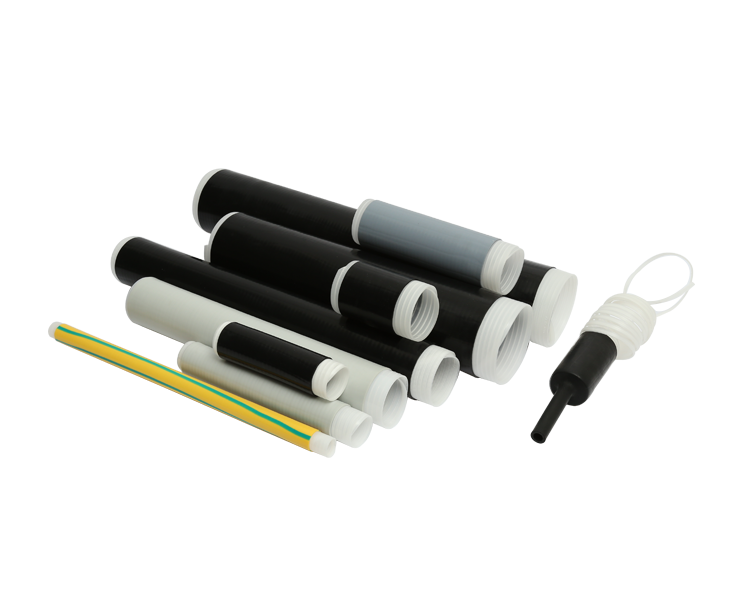
Heat Shrink Cable Sleeves are widely used in electrical and electronic applications to protect and insulate cable connections. These sleeves are made from materials that, when heated, shrink down to snugly fit around cables, creating a secure and protective barrier.
The first step in the production of heat shrink cable sleeves is the selection of suitable materials. The most common material used is cross-linked polyolefin, which provides excellent electrical insulation, chemical resistance, and environmental protection. Other materials, such as polyvinyl chloride (PVC) or fluorinated ethylene propylene (FEP), can be used for specific applications.
In this stage, the chosen material is compounded with additives to achieve the desired properties. Additives may include antioxidants, heat stabilizers, flame retardants, colorants, and other substances to enhance the performance and characteristics of the heat shrink material.
Once the material is compounded, it is fed into an extrusion machine. The extrusion process involves melting the material and forcing it through a die to create a continuous tube or sleeve. The size and thickness of the tube are determined by the design specifications, which may vary based on the intended cable size and application.
Cross-linking is a critical step in the production of heat shrink cable sleeves. The extruded material is exposed to high-energy radiation, such as electron beams or gamma rays, or it may be chemically cross-linked. This process causes the polymer chains to link together, enhancing the material's thermal and mechanical properties. Cross-linking is what allows the sleeve to shrink when heated without melting.
After cross-linking, the continuous tube is cooled to set its shape and dimensions. It is then cut into individual sleeves, each tailored to a specific length, based on the application requirements.
Some heat shrink cable sleeves may have information printed on them, such as part numbers, manufacturer details, or safety warnings. This is typically done using inkjet or hot stamp printing methods, and it helps with identification and organization during cable installations.
Heat shrink sleeves come in various shrinking ratios, such as 2:1, 3:1, or 4:1. Depending on the intended application, the sleeves may go through a final adjustment process to ensure they will shrink to the specified size when exposed to heat.
The finished heat shrink cable sleeves are packaged, typically in rolls or spools, for distribution. The packaging is designed to protect the sleeves from environmental factors and to facilitate easy handling and storage.
Throughout the production process, rigorous quality control measures are in place to ensure the sleeves meet industry standards and specific requirements. These quality checks can include:
Dimensional Inspection: Ensuring the sleeves meet the specified dimensions and shrinking ratios.
Cross-Linking Verification: Ensuring that the cross-linking process has been carried out effectively.
Physical Property Testing: Evaluating the tensile strength, elongation, and other mechanical properties.
Electrical Testing: Checking for electrical insulation properties, such as dielectric strength and volume resistivity.
Flame Retardant Testing: Assessing the flame resistance of the material.
Environmental and Chemical Resistance Testing: Determining how well the sleeves withstand exposure to moisture, chemicals, and UV radiation.
Adhesion Testing: Verifying that the sleeves adhere securely to cables after shrinking.
Once the heat shrink cable sleeves are produced and packaged, they are ready for distribution and use. During installation, the sleeves are slipped over cable connections and heated using a heat gun or other heat source. The sleeves shrink down, creating a tight and secure seal that insulates and protects the connection from environmental factors and mechanical stress.
The production process of heat shrink cable sleeves involves material selection, compounding, extrusion, cross-linking, cooling, cutting, printing, shrinking ratio adjustment, and packaging. Quality control measures are integral to ensuring that the sleeves meet industry standards and specific requirements. These versatile sleeves are essential for cable insulation and protection in various electrical and electronic applications.

 English
English 简体中文
简体中文